By NewsDesk @infectiousdiseasenews
Three cases of anthrax have been registered in the Gegharkunik region of Armenia , the Ministry of Health reports. The infections were recorded in the villages of Vanevan and Torfavan of the Vardenis region.
In two cases, the disease was recorded among the owners of infected cows, in another – from a relative of the owners.
The condition of two patients is assessed as moderate, the third is mild.
Anthrax is a bacterial pathogen in livestock and wild animals. Ruminants such as bison, cattle, sheep and goats are highly susceptible, and horses can also be infected.
Anthrax is a very serious disease of livestock because it can potentially cause the rapid loss of a large number of animals in a very short time. Affected animals are often found dead with no illness detected.
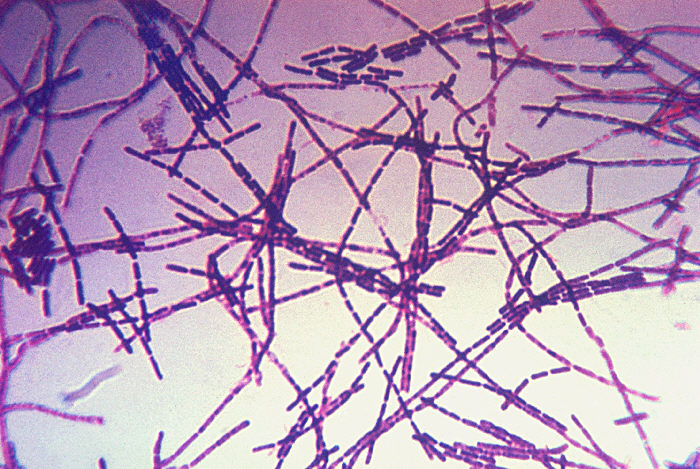
When conditions become favorable, the spores germinate into colonies of bacteria. An example would be a grazing cow ingests spores that in the cow, germinate, grow spread and eventually kill the animal. Anthrax is caused by the bacterium, Bacillus anthracis. This spore forming bacteria can survive in the environment for decades because of its ability to resist heat, cold, drying, etc. This is usually the infectious stage of anthrax.
There are no reports of person-to-person transmission of anthrax. People get anthrax by handling contaminated animal or animal products, consuming undercooked meat of infected animals and more recently, intentional release of spores.
There are three types of human anthrax with differing degrees of seriousness: cutaneous, gastrointestinal and inhalation.
- Antibiotic, Solosec, receives FDA approval as treatment of trichomoniasis
- Third death due to Naegleria fowleri in Karachi reported
- Hepatitis A cases in New Caledonia: Cases reach 300 in first half of 2021
- Eastern Equine Encephalitis: Florida reports 8th and 9th cases of 2021
- Florida reports rabies case in Volusia County horse
- China receives malaria-free certification from WHO
- Rhode Island reports Powassan virus case from Providence County
- Africa: Increase in visceral leishmaniasis cases reported in Chad


This is the 2nd occasion, of Anthrax if its a result WMD development don’t expect any neighbouring country to stay silent. Pre-emptive strikes are definitely a possibility as Armenia has used Phosphorus bombs (Banned) in Karabag so wouldn’t put it past them to go full crazy with biological weapons.