Health officials on the Caribbean island group, Turks and Caicos (TCI), are reporting a significant increase in chickenpox cases during the first four months of 2016.

Image/ M.Minderhoud
As of the end of the week of April 23, a total of 327 cases have been reported for 2016. Of these, 41 (13%) were reported by persons < 5 years old and 296 (87%) were reported by persons > 5 years old.
These cases were reported by TCI Hospital on Providenciales 234 (72%) and Grand Turk 5 (1%); with 28 cases in North Caicos and 60 (18%) cases in clinics in Providenciales. In summary, the majority cases are being reported from Providenciales (90%).
By comparison, in all of 2015, officials saw a total of 98 cases of chicken pox were reported by TCI Hospital in Providenciales.
Chickenpox is a common, usually benign childhood disease caused by the varicella-zoster virus (VZV), a member of the herpes family. This virus causes two distinct diseases; varicella (chickenpox) is the primary infection, and later when VSV reactivates,herpes zoster (shingles).
Chickenpox is highly contagious and is spread by coughing and sneezing, by direct contact and by aerosolization of the virus from skin lesions. You can also get it by contact with the vesicle secretions from shingles.
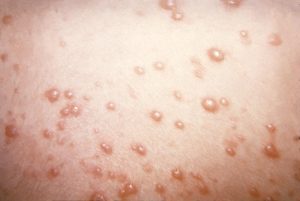
The disease is characterized by fever and a red, itchy skin rash of that usually starts on the abdomen, back or face and then spreads to nearly all parts of the body. The rash begins as small red bumps that appear as pimples or insect bites. They then develop into thin-walled blisters that are filled with clear fluid which collapse on puncture. The blisters then breaks, crusts over, and leaves dry brown scabs.
What is smallpox and how does the clinical presentation differ from chickenpox?
The chickenpox lesions may be present in several stages of maturity and are more abundant on covered skin rather than exposed. Lesions may also be found in the mouth, upper respiratory tract and genitals.
Chickenpox is contagious from 1-2 days before the rash forms and continues until all the lesions are crusted over (usually about 5 days).
This disease is more serious in adults than in children. Complications of chickenpox are rare, but includepneumonia, encephalitis and secondary bacterial infections.
Infection with this virus usually gives lifelong immunity, although second attacks have been documented in immunocompromised people. The viral infection remains latent, and disease may recur years later as shingles.
The TCI Ministry of Health strongly advises persons affected with chickenpox to remain at home during their sick leave period to prevent further spread of this illness within the community and schools.
Related:


One thought on “Chickenpox surge reported on Turks and Caicos, Providenciales hit hardest”