The McLean County Health Department has confirmed a mumps outbreak at Illinois State University as of Tuesday, March 28, 2017. A mumps outbreak, as defined by the Illinois Department of Public Health, requires at least three related cases of mumps.
Mumps is a contagious viral infection of the salivary glands that is spread through saliva or mucus. The virus can be transmitted through coughing, sneezing, or kissing. Items used by an infected person such as drinking cups, eating utensils, toothbrushes, and cigarettes, can also be contaminated with the virus and spread to others when those items are shared.
People at highest risk for mumps are those who have not received any doses of measles-mumps-rubella (MMR) vaccine and those who have received only one dose of MMR. For every 100 people vaccinated against mumps, 80 or 90 of them will be fully protected and 10 to 20 will remain at risk for the disease.
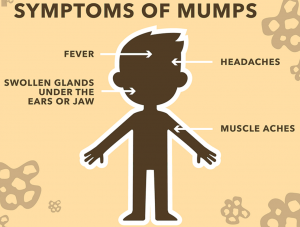
Mumps typically starts with a fever, headache, muscle aches, tiredness, and loss of appetite. Some people will have swelling of their salivary glands, which is what causes the puffy cheeks and a tender, swollen jaw.
Symptoms usually surface 16 to 18 days after infection, but individuals with mumps are actually the most contagious two days before becoming ill and for five days after.
Among males, mumps can lead to testicular inflammation that causes pain, swelling, nausea, vomiting and fever. Among some women with mumps, inflammation of the ovaries or breasts can occur. Anyone who experiences any of these symptoms should contact their doctor right away and limit their exposure to others.
Related:


One thought on “Illinois State University mumps outbreak confirmed”