By NewsDesk @infectiousdiseasenews
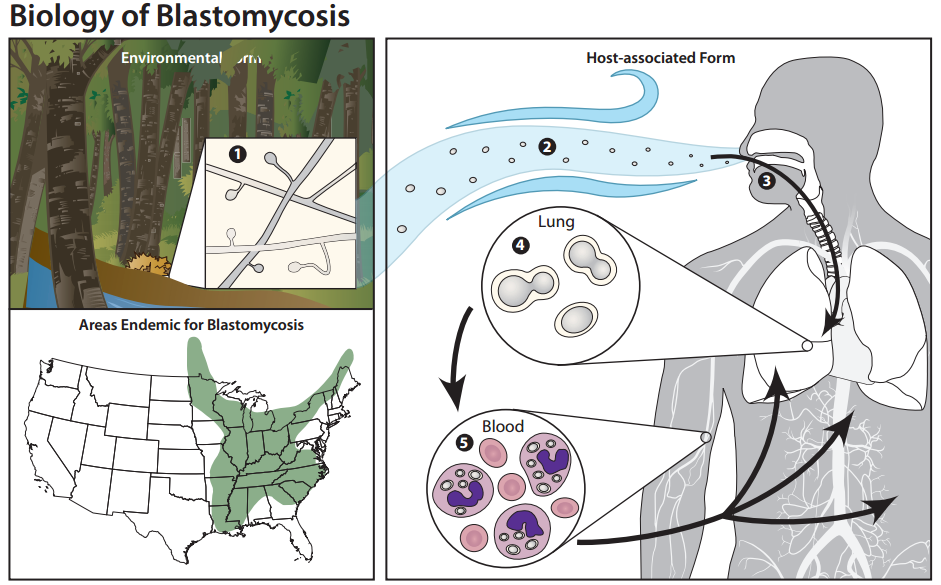
Blastomycosis is a fungal infection usually acquired by breathing in the spores of the fungi, Blastomyces dermatitidis or Blastomyces gilchristii.
In Minnesota from 1999-2018, 671 laboratory-confirmed cases of human blastomycosis were reported.
Officials note that each year, a median of 34 cases of blastomycosis are reported in Minnesota. Recently these numbers have increased; in 2018, 58 cases were reported, more than any single year during this time frame.
In Minnesota, about 1/3 of cases live and are diagnosed in a different county than where they were exposed to Blastomyces.
While most people are exposed in northern counties, or those along the Mississippi or St. Croix Rivers, people can be exposed to Blastomyces in many counties across the state.
Approximately 10% of cases die of blastomycosis.
Blastomyces dermatitidis can be found throughout the world, but is most common in parts of North, Central, and South America. In the United States, the fungus is endemic in the Southeast and the Midwest.
The time between exposure to the spores and when symptoms develop varies widely, ranging from 21 to 100 days. About 50% of infections are asymptomatic (no symptoms).
When symptoms of blastomycosis are present, they may include: Fever, cough, or cough with blood, shortness of breath, muscle aches, bone pain, back pain, chest pain, fatigue, weight loss, chills and/or night sweats and skin sores.
Minnesota reports hepatitis A outbreak, 29 states now reporting
Minnesota reports most congenital syphilis cases ever
Acute flaccid myelitis in Minnesota: An interview with Michael Osterholm, PhD



My late dad, Silas Tungesvik, Radcliffe, Iowa, was diagnosed with blastomycosis around 1957+.
He was paralyzed from his neck down and in an area hospital for 30 days. (Twice in his life he was paralyzed from his neck down and recovered fully!)
When he got out, he couldn’t even reach his hand across the table to get something to eat.
He had to drink IODINE several times daily.
What all his symptoms, diseases, etc. throughout his life, I realize now he had SEVERAL TICK-BORNE DISEASES never diagnosed.
I know this because I’ve had chronic LYME DISEASE FOR 50.5 YEARS; 35 years MISDIAGNOSED by 40-50 yrs.
2018 diagnosed with BARTONELLA aka cat scratch disease, 2 species…a 2nd tick-borne disease since pathologist found bart in my husband’s 2nd brain autopsy.