In late February, Tropical Cyclone Winston raked across the island of Fiji as a Category 5 storm with maximum sustained winds of 180 mph, becoming the first such storm on record to hit the island.
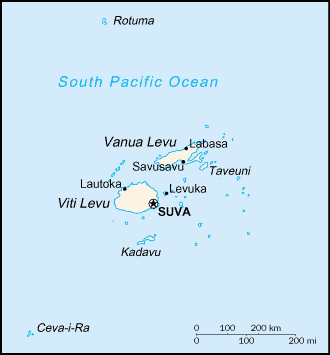
The damage was immense. 44 people died on Fiji and neighboring islands and on Fiji, some 55,000 homes were damaged or destroyed and approximately 350,000 people—roughly 40 percent of Fiji’s population—were significantly impacted by the storm.
In the aftermath of the storm, Fiji health officials are now reporting a typhoid fever outbreak in the Central Division. To date, 25 confirmed (Sixteen cases were recorded in Qelekuro, three in Nabulini, five in Veicorocoro and one in Luvunavuaka) and 21 suspected cases have been reported.
“The Ministry of Health and Medical Services is aware of these cases and our team based in Korovou is on the ground visiting the affected sites on a daily basis,” permanent secretary for Health Meciusela Tuicakau said yesterday.
Related: Fiji outbreak: Pink eye cases increase to 5000
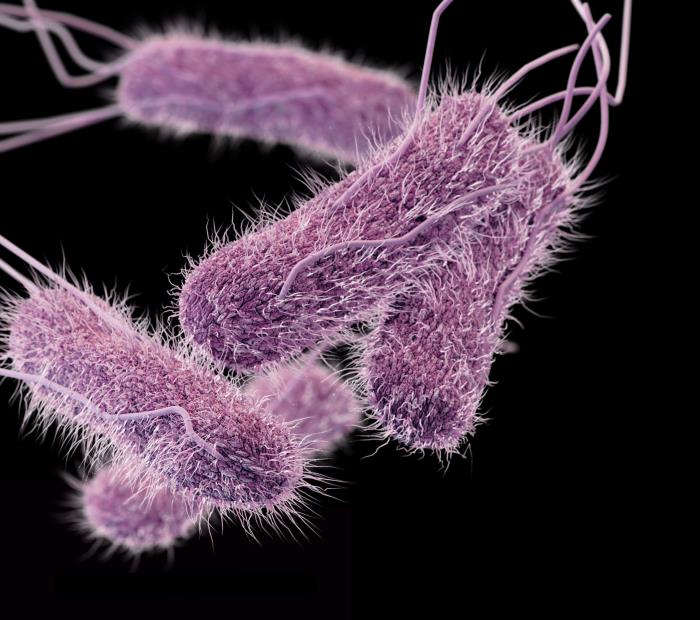
Typhoid fever, caused by the bacterium Salmonella typhi, is a life-threatening bacterial infection. Typhoid fever is still common in the developing world, where it affects about 21 million people annually.
Salmonella typhi lives only in humans. Persons with typhoid fever carry the bacteria in their bloodstream and intestinal tract. In addition, a small number of persons, called carriers, recover from typhoid fever but continue to carry the bacteria. Both ill persons and carriers shed S.typhi in their feces.
You can get typhoid fever if you eat foodor drink beverages that have been handled by a person who is shedding S. typhi or if sewage contaminated with S. typhi bacteria gets into the water you use for drinking or washing food. Therefore, typhoid fever is more common in areas of the world where handwashing is less frequent and water is likely to be contaminated with sewage.
Typhoid fever can be successfully treated with appropriate antibiotics, and persons given antibiotics usually begin to feel better within 2 to 3 days.
Learn more about typhoid fever in this educational video
Related:
- CDC issues travel notice for the island of Kosrae due to Zika transmission
- Yellow fever update: 1400 suspected cases, nearly 200 deaths in Angola
- São Paulo: 18 blinded after cataract surgery campaign; Pseudomonas contaminated instruments implicated


4 thoughts on “Typhoid fever: Fiji outbreak reported in aftermath of Tropical Cyclone Winston”