Hong Kong health officials (CHP) are advising the public to remain vigilant with personal hygiene as the city enters the peak season of hand, foot and mouth disease (HFMD) and enterovirus 71 (EV71) infection.
Image/shawn c
“The activity of both HFMD and EV71 infection is on the rise. The usual peak season is from May to July, with a possible smaller winter peak from October to December. Schools, institutions and play facilities should observe our guidelines and health advice against outbreaks to better protect young children who are more prone to both diseases,” a spokesman for the CHP said.
The number of institutional HFMD outbreaks increased from five (affecting 16 persons) in the week ending April 30 to 30 (124 persons) last week. As of yesterday (May 17), 13 (42 persons) had been reported this week. In the past four weeks, kindergartens and child care centres (KG/CCCs) reported most outbreaks (63 per cent), followed by secondary schools (20 per cent) and primary schools (17 per cent).
As for EV71 infection in 2016, as of yesterday, three cases were recorded with no severe or death cases. In 2015, 56 cases including six with severe complications were filed. Regarding severe pediatric enterovirus infection other than EV71 and poliovirus, three cases had been recorded so far this year while eight were recorded in 2015, with no deaths in both years.
Health officials also note some neighboring areas have also entered the peak season since late April. The Health and Family Planning Commission of Guangdong Province reported 88,366 HFMD cases to date, including three deaths, rising 72 per cent from last year. In Taiwan, according to the Centers for Disease Control, the EV activity is increasing and 17 000 EV consultations were recorded last week, rising 27.8 per cent from the preceding week.
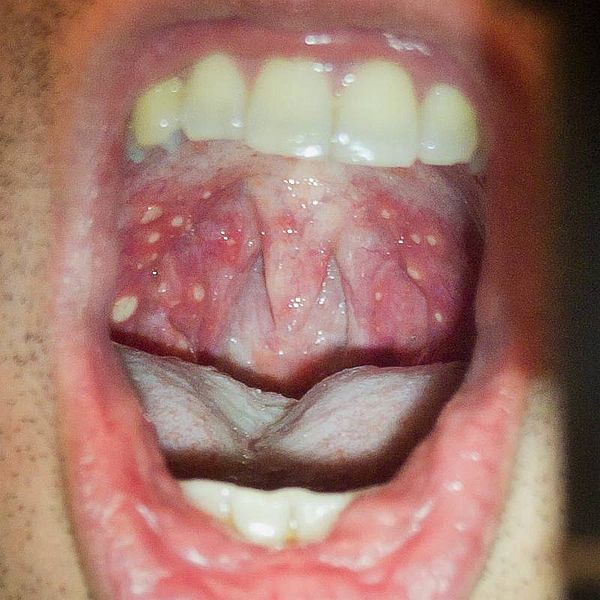
“HFMD is common in children and is usually caused by EVs such as Coxsackievirus and EV71. It is clinically characterized by maculopapular rash or vesicular lesions occurring on the palms, soles and other parts of the body such as the buttocks and thighs. Vesicular lesions and ulcers may also be found in the oral cavity. Sometimes patients present mainly with painful ulcers at the back of the mouth, namely herpangina, without rash on the hands or feet,” a CHP spokesman said.
Related:
- Tokyo reports TB outbreak
- Taiwan reports increases in enterovirus, hepatitis A infections
- China: 11 additional H7N9 avian influenza cases reported


One thought on “Hand, foot and mouth disease: Hong Kong hits peak season”