The Marshall Islands Health Department reports that mumps may have infected up to 3,000 people since March, according to a local media account, making it the largest outbreak reported in decades.
According to the Marianas Variety report, the official number of confirmed and probable cases is now 1,033 since March; however, health officials warn the true number of cases could be as high as 3,000.
The bulk of the cases have been reported in the capital and largest city of Majuro (844), while nearly 200 cases have been reported in Ebeye.
This follows the large mumps outbreak in northwest Arkansas, where a large number of Marshallese people live. The 2nd-largest U.S. continental population of Marshallese is concentrated in Springdale (Washington and Benton Counties). Arkansas has seen about 3000 cases since last year.
A vaccination campaign began in April in Majuro and Ebeye and additional campaigns are being conducted in Arno, Mejit, Utrik, Ailinglaplap, Namu and Ailuk.
Mumps is spread by droplets of saliva or mucus from the mouth, nose, or throat of an infected person, usually when the person coughs, sneezes or talks. Items used by an infected person, such as cups or soft drink cans, can also be contaminated with the virus, which may spread to others if those items are shared.
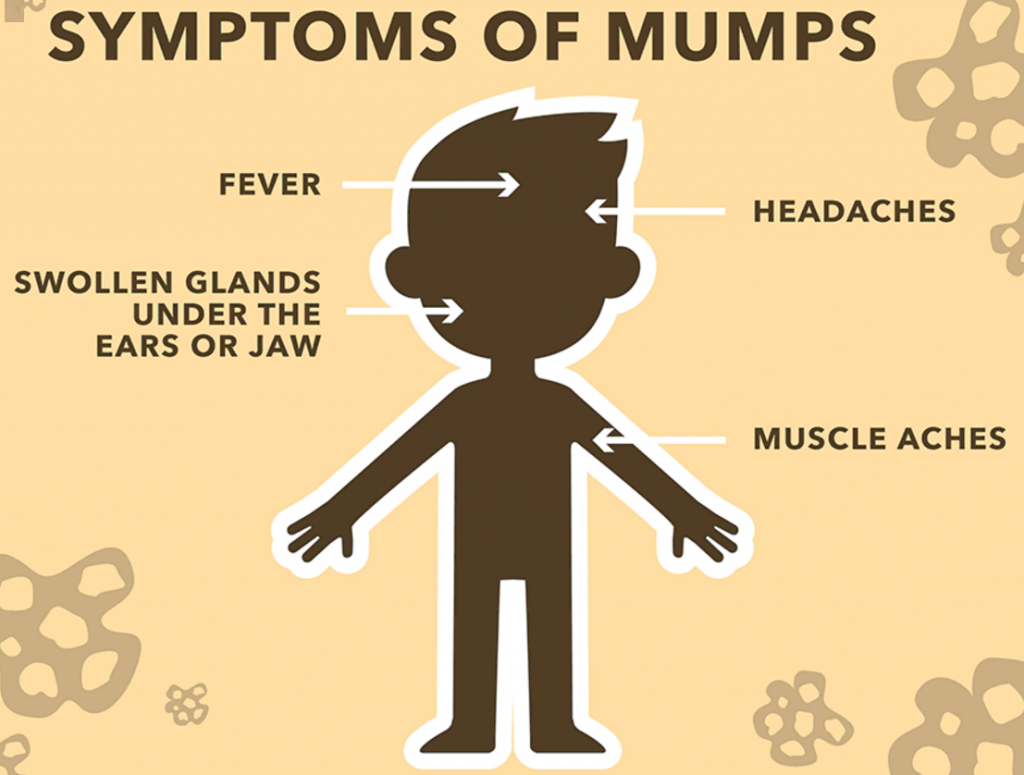
Symptoms typically appear 16-18 days after infection, but this period can range from 12-25 days after infection. It is usually a mild disease, but can occasionally cause serious complications.
The most common complication is inflammation of the testicles (orchitis) in males who have reached puberty; rarely does this lead to fertility problems.
Other rare complications include inflammation of the brain and/or tissue covering the brain and spinal cord(encephalitis/meningitis), inflammation of the ovaries (oophoritis) and/or breasts (mastitis) in females who have reached puberty and deafness. Anyone who is not immune from either previous mumps infection or from vaccination can get mumps.
Related:


