A Legionnaires’ disease outbreak at a Lisbon hospital has now infected 26 patients and two hospital employees, according to Health Minister, Adalberto Campos Fernandes today as reported in a Expresso report (computer translated).
All the patients reportedly were from one unit and had underlying risk factors.
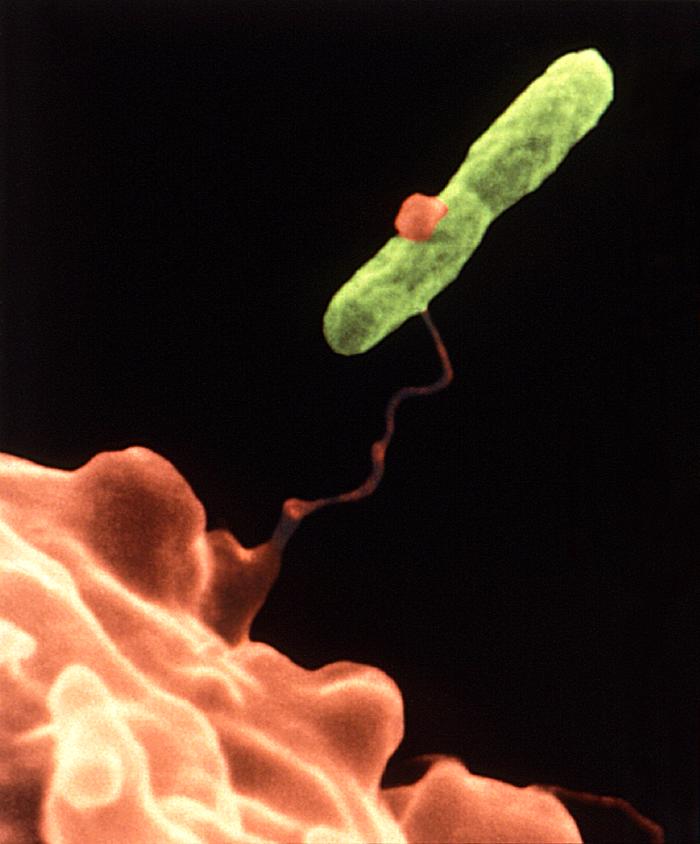
The outbreak reported at São Francisco Xavier Hospital in Lisbon is already the largest in a hospital unit in Portugal and one of the largest in the world and more positive cases are expected.
The Health Minister admitted that “something had gone wrong”, but told local reporters that he was confident the hospital had been following the best practices.
An investigation into the cause of the outbreak has been opened.
LISTEN:
Legionnaires’ disease is caused by the bacteria Legionella. Symptoms include fever, cough, chills, muscle aches, headache, fatigue, loss of appetite, confusion and diarrhea. Symptoms usually appear two to 10 days after significant exposure to Legionella bacteria. Most cases of Legionnaires’ disease can be traced to plumbing systems where conditions are favorable for Legionella growth, such as cooling towers, whirlpool spas, hot tubs, humidifiers, hot water tanks, and evaporative condensers of large air-conditioning systems.
Legionnaires’ disease cannot be spread from person to person. Groups at highest risk for Legionnaire’s disease include people who are middle-aged or older, especially cigarette smokers, people with chronic lung disease or weakened immune systems and people who take medicines that weaken their immune systems (immunosuppressive drugs). Those with symptoms should call their doctor and ask about testing for Legionnaire’s disease.
Related:
- 52 million children living with viral hepatitis globally: New data
- Cholera, polio vaccination drive enters 2nd phase for Rohingya population at Cox’s Bazar
- Miami: Sexually transmitted Zika case confirmed
- Ebola aid money fraud: Red Cross statement
- Nebraska reports first H3N2v ‘swine’ flu case
- LA health officials urge gay men to get vaccinated for hepatitis A

