Officials with the University of Kansas Watkins Health Services have reported an increase in sexually transmitted infections (STIs), in particular gonorrhea over the past year, according to a Lawrence World-Journal report.
The number of gonorrhea cases rose 39 percent from 2016 to 2017, the report notes.
All STIs are up in the whole of Douglas County, KS.
According to Jenny McKee, program manager at Watkins’ Health Education Resource Office, local health officials attributed the spike in recorded cases partly to changing sexual behaviors and partly to increases in STD testing.
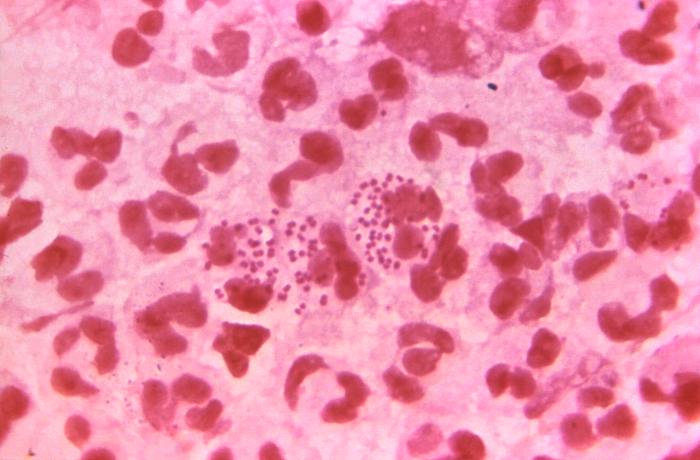
Gonorrhea is a sexually transmitted infection (STI) caused the bacterium, Neisseria gonorrhoeae. This bacterium can infect the genital tract, mouth and rectum of both men and women. Ejaculation does not have to occur for the disease to be transmitted. It can also be transmitted from mother to baby during delivery.
Symptoms of gonorrhea usually appear with 2 to 5 days after sexual contact with an infected partner, occasionally symptoms make take longer to appear.
In women, infection may be asymptomatic. If present, the early symptoms of gonorrhea are often mild. The first symptoms in women are frequently; painful or burning sensations when urinating, an increase in discharge (yellow or bloody) and bleeding after intercourse.
Men have symptoms more often than women and they may include; a white, yellow or green discharge from the penis with pain, burning sensations during urination, and painful, swollen testicles.
While infection of the throat and rectum are frequently asymptomatic, rectal infection may have discharge, itching and painful bowel movements. The complications of untreated gonorrhea are numerous. The most common being pelvic inflammatory disease (PID), a serious infection of the female reproductive tract.
Ectopic pregnancy may occur due to scar tissue that’s formed in the fallopian tubes. This can result in miscarriage or death of the mother.
In men, untreated gonorrhea can cause epididymitis, a painful condition of the testicles that can lead to infertility. Rarely, untreated gonorrhea can spread through the blood to the joints, causing permanent joint damage (gonococcal arthritis). Problems for the newborn that gets gonorrhea during delivery are blindness, joint and blood infections. When a child has the infection in any part of the body, it’s most commonly due to sexual abuse.
N. gonorrhoeae has progressively developed resistance to each of the antimicrobials used for treatment of gonorrhea. Most recently, declining susceptibility to cefixime resulted in a change to the CDC treatment guidelines, so that dual therapy with ceftriaxone and either azithromycin or doxycycline is now the only CDC-recommended treatment regimen for gonorrhea. The emerging threat of cephalosporin resistance highlights the need for continued surveillance of N. gonorrhoeae antimicrobial susceptibility.
Related:



3 thoughts on “University of Kansas reports increase in gonorrhea”