Nunavut communities, especially those in the Kitikmeot, have seen an increase in cases of Gonorrhea.
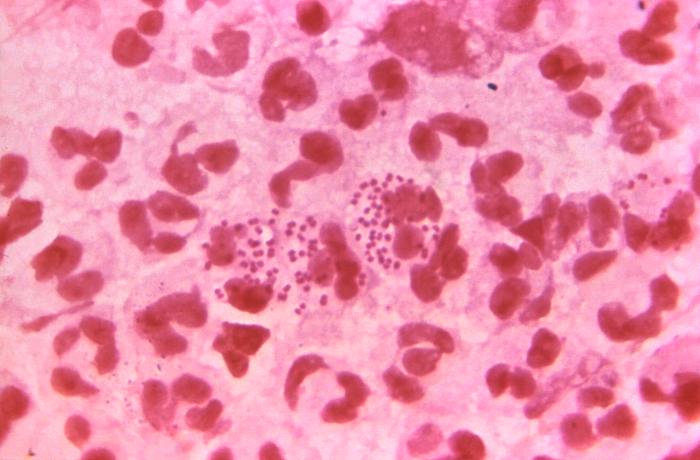
Gonorrhea is a sexually transmitted infection (STI) that is passed through sexual contact. You can help prevent the spread of gonorrhea in your community by practising safer sex (like wearing a condom), getting tested, being mindful about your sexual partners (the more partners you have, the more at risk you are), and getting treatment when needed.
Gonorrhea is treatable with antibiotics. However, if not treated it can cause chronic pelvic pain in women and infertility in both men and women. People with untreated gonorrhea are also at greater risk of getting another sexually transmitted infection.
It is important to be tested if you think you have gonorrhea or another STI. Common symptoms of gonorrhea in men include discharge from the penis. In women, symptoms include pain while urinating or vaginal discharge. Many individuals have no symptoms with gonorrhea but are still at risk of complications.
Gonorrhea is easily tested for and treated.
Toronto officials report 1st human West Nile virus case
Canada: Crab cakes, Tarragon Remoulade recalled due to Salmonella risk
Cyclospora outbreak cases rise to 690, FDA updates investigation
Canada: Chickenpox reported at Children’s Hospital of Eastern Ontario

