In a follow-up on the chikungunya outbreak in Kassala State, Sudan, government officials in Kassala report an increase in cases of 23 per cent in a week, according to a local media account.
Kassala state government reported one week ago that 10,900 people were infected in the state during the past weeks. The most recent tally puts the case count at 13,400.
Reports on social media put the death toll at 150; however, these numbers are unverified.
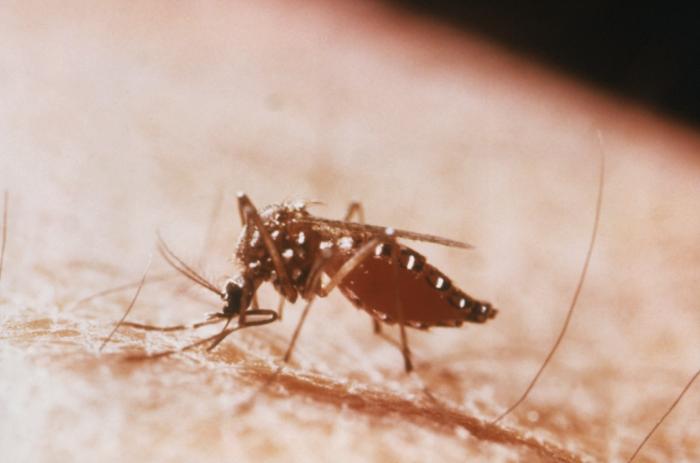
Chikungunya virus is transmitted by the bite of Aedes mosquitoes, particularly Aedes aegypti and Aedes albopictus. In humans bitten by an infected mosquito, the disease symptoms usually appear after an incubation period of three to seven days (range 1- 12 days).
CHIKV can cause acute, sub-acute, and chronic disease.
In acute disease, symptoms develop abruptly and include high fever, headache, myalgia and arthralgia (predominantly in limbs and large joints). The appearance of a maculopapular rash is also frequent. Severe forms of the disease are rare. Symptoms usually resolve in 7-10 days, although arthralgia and joint stiffness may persist intermittently for several months.
The disease shares some clinical signs with dengue and Zika, and can be misdiagnosed in areas where they are common. As there is no cure, treatment is focused on relieving the symptoms.
- Monkeypox and hepatitis E outbreaks reported in the Central African Republic
- South Sudan rolls out Rotavirus sentinel surveillance sites
- Red Cross workers attacked during safe burial of Ebola victim in DR Congo
- Madagascar plague: Bubonic and pneumonic cases confirmed
- South Africa reports the most human rabies in 10 years


