Hong Kong health officials urged the public to maintain strict personal and environmental hygiene as the local activity of hand, foot and mouth disease (HFMD) and enterovirus (EV) 71 infection has been increasing in the past two weeks.
Image/shawn c
According to the Centre for Health Protection (CHP) of the Department of Health, the number of institutional HFMD outbreaks recorded increased from five (affecting 23 persons) to 14 (affecting 60 persons) from the week of May 6 to that of May 13. As of May 24, 15 outbreaks involving 59 persons had been reported this week. In the last four weeks, most outbreaks occurred in kindergartens and child care centres as well as primary schools.
As for EV71 infection, while only one case of infection was recorded per month in February and March this year, the number of cases increased to seven in May, bringing the total to nine cases this year.
“HFMD occurs throughout the year. Apart from a summer peak from May to July, a smaller peak may also occur from October to December. As young children are more susceptible, parents should stay alert to their health. Institutional outbreaks may occur where HFMD can easily spread among young children with close contact,” a spokesman for the CHP said.
“We have issued letters to doctors, child care centres, kindergartens and primary and secondary schools to alert them to the latest situation. Schools are reminded to follow the Guidelines on Prevention of Communicable Diseases on preventive and control measures as well as management of outbreaks, which should be reported to the CHP for prompt follow-up,” the spokesman added.
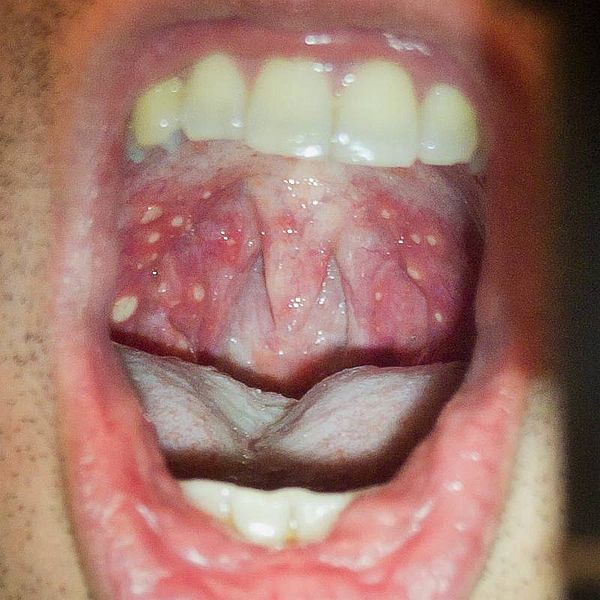
HFMD is typically a benign and self-limiting disease. Most common in young children, it presents as fever, oral lesions and rash on the hands, feet and buttocks. The oral lesions consist of rapidly-ulcerating vesicles on the buccal mucosa, tongue, palate and gums. The rash consists of papulovesicular lesions on the palms, fingers and soles, which generally persist for seven to 10 days, and maculopapular lesions on the buttocks.
China FDA approves EV71 vaccine, HFMD in Asia
Hand, foot, and mouth disease is caused by viruses that belong to the Enterovirus genus (group). This group of viruses includes polioviruses, coxsackieviruses, echoviruses, and enteroviruses.
EV-71 has been implicated in HFMD outbreaks in Southeast Asia over the several years. EV 71 is a non-polio enterovirus.
Complications associated with HFMD caused by the more pathogenic EV-71 strain include encephalitis, aseptic meningitis, acute flaccid paralysis, pulmonary edema or hemorrhage and myocarditis. Most deaths in HFMD occur as a result of pulmonary edema or hemorrhage.
Related:
- DRC Ebola outbreak update
- India: Additional Nipah death reported in Kozhikode
- Indiana: Deer ticks found in increased numbers in the southern part of the state
- North Carolina reports increase in hepatitis B and C cases
- Hanoi: Dengue cases down, HFMD cases up in 2018
- Reunion reports an additional 400 dengue cases
- Salmonella outbreak linked to kratom over: 199 cases in 41 states
- Nipah virus: $25 million agreement to advance the development and manufacture of a vaccine


