In a follow-up on the measles outbreak in Limerick City, Ireland, the Health Service Executive (HSE) has confirmed nineteen measles cases in the city since the beginning of the year. There is also a case in Dublin linked to the outbreak. Nine cases have been children aged zero to five years, all unvaccinated, four of whom were admitted to hospital. Eleven cases have been aged between 15 and 34 years, all but 2 had no MMR vaccines, and four were admitted to hospital.
An Outbreak Control Team made up of representatives from the HSE is involved in managing the outbreak in an effort to prevent further spread. The measures taken include active follow up of confirmed or suspected cases and their contacts, protection of vulnerable contacts (e.g. pregnant women who are not immune to measles and babies who are too young to have been immunised) and encouraging vaccine uptake in those who are not fully vaccinated through additional school and community vaccination clinics.
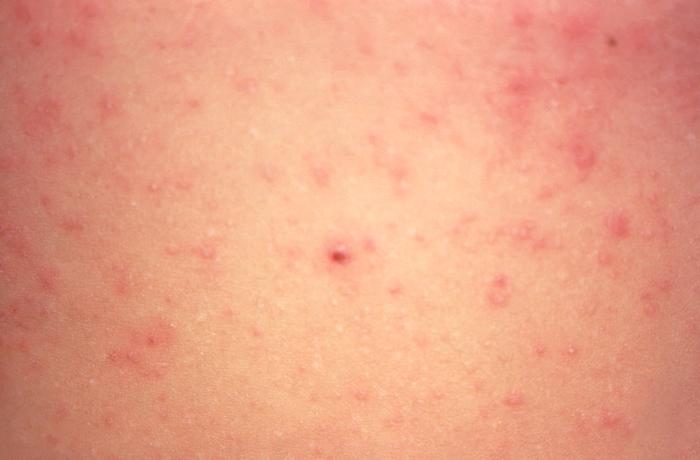
Measles is a viral illness that is spread through direct contact and through the air. It is highly contagious and is spread easily. One case of measles can infect 15-20 unvaccinated people. While the numbers of cases of measles in Ireland has reduced dramatically since the introduction of the measles vaccine, it remains a significant cause of death among young children worldwide.
Europe measles cases up 400 percent in 2017
People most at risk of catching measles are those who either have not had measles infection in the past, those who are not fully vaccinated with 2 doses of MMR vaccine (in particular babies younger than 12 months who are too young to be vaccinated), and those with weakened immune systems. Anyone who has been exposed and is not immune to measles may develop measles up to three weeks following date of exposure.
The primary strategy for measles control is achieving a high level of immunity in the population with age appropriate MMR vaccination. MMR uptake at 24 months of age is 88% in Limerick and is 93% for the Mid West. An uptake rate of 95% is required for effective immunity within a population. This level of vaccination protects those who cannot be vaccinated by reason of age, pregnancy or illness.


