The state of Johor, located on the southern portion of the Malaysian peninsula, has reported more than a 15% increase in dengue fever this January as compared to Jan. 2014.
According to the National News Agency of Malaysia, a total of 701 cases of dengue fever were reported in Johor with two deaths recorded for the first four weeks of this year.
State Health and Environment Committee chairman Datuk Ayub Rahmat said this is up 15.5 percent, compared to 591 cases for the same period last year.
Two fatalities were reported in Johor in Jan. 2014 also.
Ayub said a total of 6,324 cases of dengue fever were recorded throughout the state last year, compared with 4,828 cases in 2013, with 24 fatalities recorded for each year.
Malaysia was hit extra hard with dengue fever in 2014 with about 100,000 cases nationwide, three times the number recorded in 2013.
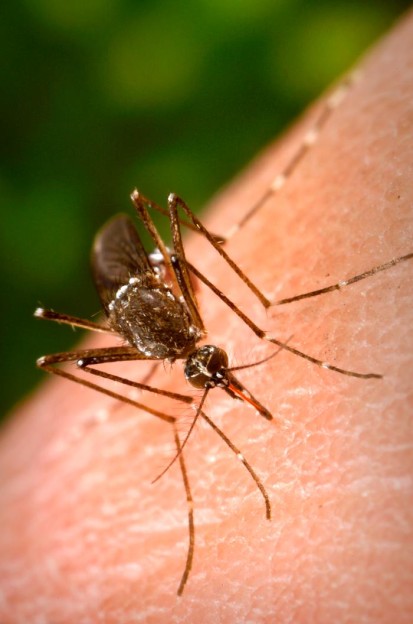
People get the dengue virus from the bite of an infected Aedes mosquito. It is not contagious from person to person.
There are three types of dengue fever in order of less severe to most: the typical uncomplicated dengue fever, dengue hemorrhagic fever (DHS) and dengue shock syndrome (DSS).
The World Health Organization (WHO) estimates there may be 50–100 million dengue infections worldwide every year. However, new research from the University of Oxford and the Wellcome Trust, using cartographic approaches, estimate there to be 390 million dengue infections per year worldwide.
For more infectious disease news and information, visit and “like” the Infectious Disease News Facebook page


One thought on “Johor State, Malaysia reports 700 dengue fever cases in January”