NewsDesk @bactiman63
The European Centre for Disease Prevention and Control (ECDC) reported in their latest Monkeypox situation update that during the week ending September 4, decreases in notification rates were reported by 20 countries, with the largest decrease in Cyprus, Estonia, and Luxembourg.
Increases in notification rates were reported by four countries (Bulgaria, Finland, Slovakia, and Slovenia).
Since the start of the monkeypox outbreak, and as of 20 September 2022, 19,827 confirmed cases of monkeypox (MPX) have been reported from 29 EU/EEA countries.
The five countries that have reported the most cases since the start of the outbreak are: Spain (7083), France (3897), Germany (3570), the Netherlands (1221) and Portugal (845). Five deaths have been reported.
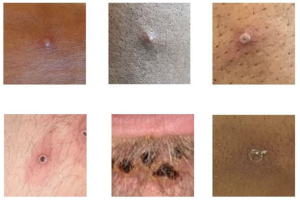
MPX cases continue to be primarily reported among men who have sex with men (MSM) aged between 18–50 years.
Although some severe cases (including encephalitis) have been reported during the current outbreak, the impact of the disease remains low for most cases, the ECDC reports.
Globally, the World Health Organization (WHO) reports since 1 January 2022, cases of monkeypox have been reported to WHO from 105 Member States across all 6 WHO regions. As of September 20 2022, a total of 62,532 laboratory confirmed cases and 1,667 probable cases, including 23 deaths, have been reported to WHO.
Since 13 May 2022, a high proportion of these cases have been reported from countries without previously documented monkeypox transmission. This is the first time that cases and sustained chains of transmission have been reported in countries without direct or immediate epidemiological links to areas of West or Central Africa.
With the exception of countries in West and Central Africa, the ongoing outbreak of monkeypox continues to primarily affect men who have sex with men who have reported recent sex with one or multiple partners. At present there is no signal suggesting sustained transmission beyond these networks.
- Chikungunya cases up 573% in the Philippines in 2022
- Laos dengue outbreak tops 25,000 cases
- Uganda declares Ebola (Sudan) outbreak in Mubende District
- Malawi eliminates blinding trachoma, Fifth African country to achieve this significant milestone
- Philippines reports 271% increase in cholera in first 8 months of 2022
- Mongolia: Human plague case reported in Khovd province
- Ebola outbreak declared in Uganda
- Alabama reports the most congenital syphilis cases in 15 years
- Dengue fever cases in Hanoi increased 4.5 times, Vietnam total tops 200K

