By NewsDesk @bactiman63
Eleven outbreaks of hand-foot-mouth disease (HFMD) were registered by the Municipality of Campinas, São Paulo State this month, in early childhood education schools both in public and private.
Image/shawn c
According to the Administration, the outbreak is a recording of two or more cases of the disease. The syndrome is an infection caused by the Coxsackie virus and affects children, especially those under five years of age.
The infectologist and coordinator of Epidemiological Surveillance (Devisa), Valéria Almeida, said cases of the disease are common and that outbreaks are occurring because of the children’s return to schools after months at home and without contact with the rest of the school community.
Subscribe to Outbreak News TV on YouTube
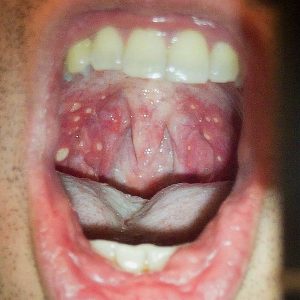
HFMD is typically a benign and self-limiting disease. Most common in young children, it presents as fever, oral lesions and rash on the hands, feet and buttocks. The oral lesions consist of rapidly-ulcerating vesicles on the buccal mucosa, tongue, palate and gums. The rash consists of papulovesicular lesions on the palms, fingers and soles, which generally persist for seven to 10 days, and maculopapular lesions on the buttocks.
It is spread to others by close personal contact, coughing or sneezing or by contact with contaminated objects and surfaces. It can be difficult to eradicate in schools, group living communities and daycares. Although it is not serious for most people, the infection can cause significant pain while eating, walking and writing.
Hand, foot, and mouth disease is caused by viruses that belong to the Enterovirus genus (group). This group of viruses includes polioviruses, coxsackieviruses, echoviruses, and enteroviruses. Coxsackievirus is the most common cause of HFMD.
- United Kingdom reports first cases of Omicron variant
- Philippines records less than 1000 COVID-19 cases for 4th day in a row, Monitoring for Omicron
- Global syphilis population made up of two lineages: Study
- Omicron COVID-19 variant: Africa CDC statement
- Vietnam reports 13,109 new COVID-19 cases, Monthly total tops in SE Asia
- Philippines reports more than 60K dengue cases so far, One of the highest totals globally
- WHO designates B.1.1.529 as a VOC, named Omicron
- Hong Kong starts strict quarantine requirements for travelers from eight southern African countries
- Finland advises avoiding all travel to southern Africa

