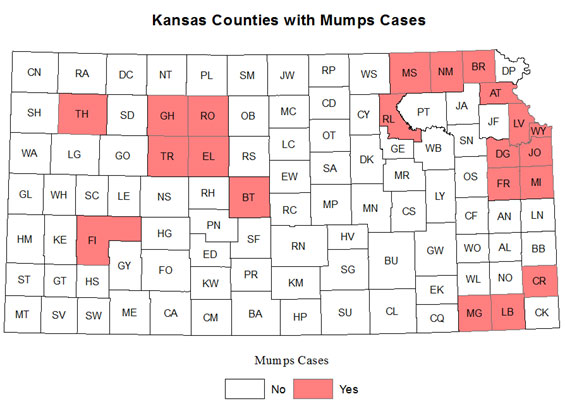
Kansas health officials are now reporting 120 mumps cases in the state, affecting 21 counties to date.
Of the counties reporting the most cases, Marshall has reported 21 cases. This is followed by Riley and Johnson Counties with 17 each and Douglas and Crawford counties reporting 16 and 15 cases, respectively.
Ten cases experienced complication from mumps and one person required hospitalization for their illness.
Like in many other outbreak reported across the country, most of the cases were vaccinated.
LISTEN: Mumps: Canada, the virus and the vaccine and why the comeback
The Kansas Department of Health Environment (KDHE) and affected local health departments are working closely together to identify cases and implement appropriate isolation and exclusion policies to prevent further spread of mumps. Many cases are associated with participating in sports, including wrestling and basketball, in Kansas. There are also associations with the University of Kansas, Kansas State University, and travel to other states that are currently experiencing large mumps outbreaks.
Mumps is an acute viral infection. Transmission occurs from person to person through coughing, sneezing, or talking; by sharing items such as cups or utensils with others; or by touching objects or surfaces freshly soiled by infected respiratory secretions.
Symptoms typically begin with body aches, loss of appetite, fatigue, headache, and low grade fever, and may progress to parotitis (swollen parotid salivary gland/s). Parotitis can occur on one or both sides, or not be present at all. Earache on the side of parotitis and discomfort with eating acidic foods are common. Most persons with mumps will recover completely though serious complications can occur.
Complications include orchitis (testicular inflammation in males), oorphritis (ovarian inflammation in females), aseptic meningitis (inflammation of the lining of the brain), and rarely encephalitis (inflammation of the brain), pancreatitis, deafness, and death.
Symptoms usually appear 16-18 days after being infected with the mumps virus, but can range from 12- 25 days after being infected. Persons with mumps are considered contagious two days before through five days after parotitis onset. If parotitis is not present, persons are considered contagious for eight days following onset of first symptoms.
Related:


One thought on “Kansas reports 120 mumps cases in 21 counties”