NewsDesk @bactiman63
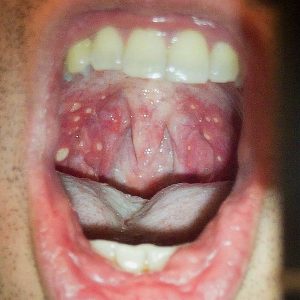
In a follow-up on the hand, foot and mouth disease (HFMD) outbreak in Malaysia, the Ministry of Health reports through May 21, a total of 47,209 cases of HFMD, which is a 20 -fold increase compared to 2021 during the same period, which saw only 2,237 cases.
Image/shawn c
While the cases reported for epi week 20/2022 were 15,548 cases compared to epi week 19/2022 which was only 7,526 cases nationwide, an increase of 106.6%. An increase in cases on epi week 20 was expected due to the movement of Malaysians during the Hari Raya celebrations.
In 2022, until 21 May 2022, the State of Selangor contributed the largest number of cases compared to other states which was 13,640 cases (28.9%). It is followed by WP Kuala Lumpur & Putrajaya 6,206 cases (13.1%), Perak 4,099 cases (8.7%), Kelantan 3,726 cases (7.9%) and Sabah 3,352 cases (7.1%) while other states around or less than 2,500 cases.
HFMD cases are common among children aged 6 years and below which is 43,736 cases (93%), followed by the age group 7 to 12 years which is 2,765 cases (6%). While the rest are over 12 years old which is 708 cases (1%).
Based on the type of virus (enterovirus) surveillance in Malaysia, the three (3) major viruses that cause the spread of HFMD in the community in 2022, are Coxsackie A16 (CA16), Coxsackie A6 (CA6) and Enterovirus 71 (EV71). In 2022, to date, there have been two (2) EV71 -positive HFMD cases admitted to the ICU due to complications of encephalitis. Both cases were children under 6 years of age.
The State Health Department and the District Health Office have conducted sessions with agencies overseeing the management of nurseries, kindergartens and pre-schools, in addition to issuing alert letters. The session has been held since epi week 17/2022 following the increase in HFMD cases in most states. Sessions are made in the form of townhall sessions, webinars, briefings and demonstrations especially related to the disinfection process.
Dengue cases up 45% in Malaysia
During this session as well, emphasis is given to:
- Screening at the entrances of kindergartens, kindergartens and pre-schools (gate-keeping) to ensure there are no signs of HFMD infection before children are allowed to enter the premises.
- Practice hand washing with soap and clean water after going to the toilet, after changing diapers, and after touching / treating blisters and while washing the child’s stool.
- Nursery, kindergarten and pre-school operators are advised to provide suitable hand washing facilities.
- Cleaning and disinfecting children’s toys and house floors, especially toilets, using chlorine based solution.
- Proper management of disposable diapers by disposing of them in a covered trash can.
- Use separate eating and drinking utensils and do not share items with other children.
Related:
Vietnam: Dengue cases up 33% in Ho Chi Minh City
North Korea COVID-19 update according to state media
Singapore closes in on 10,000 dengue cases
H5N6 avian influenza case reported in Guangxi, China

