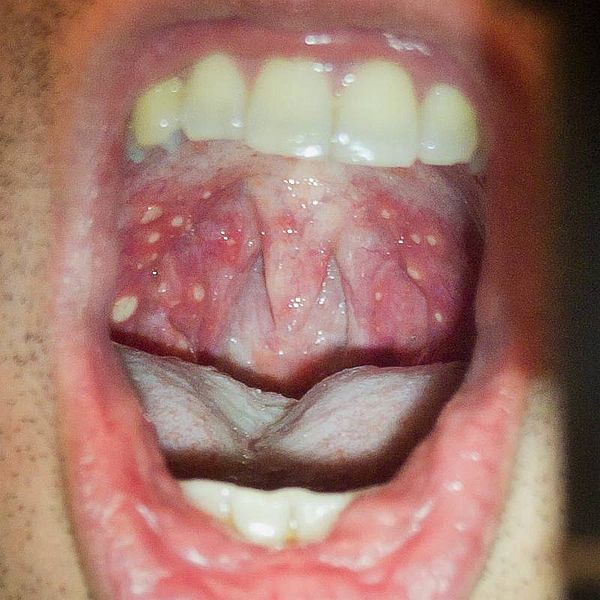
The Vietnam Ministry of Health reported recently that since the beginning of the year, the country has recorded 10,745 cases of hand, foot and mouth disease (HFMD) in 63 provinces and cities, including 6,662 cases of hospitalization and no deaths.
Compared to the same period in 2019, the number of cases nationwide decreased by 55.6%, the number of hospitalized cases decreased by 51.5%, but some provinces and cities recorded an increase in the number of cases in recent weeks such as Ho Chi Minh City.
Image/shawn c
Officials predict HFMD cases are likely to increase due to the nature of the transmission, especially with the school year starting.
Health officials have instituted the following to proactively prevent and combat hand-foot-and-mouth disease:
1. To advise the People’s Committees of provinces and cities in directing administrations at all levels, mobilizing committees, branches, organizations, socio-politics to closely coordinate with the health sector in drastically and synchronously implementing effective measures to prevent and control epidemics in the area, focusing on areas with high numbers of cases and risk of outbreaks.
2. Strengthening health education and communication, actively deploying patriotic sanitation activities to improve people’s health; perform 3 cleanings: eat clean, stay clean, clean hands and play clean toys; organize soap hand washing campaign, implement food hygiene and safety, eat and drink hygiene, eat and drink nine; propagating measures to prevent and spread hand, foot and mouth infection in various forms such as meetings of local people groups, mass meetings, on-the-job training, instruction, flyers, radio, radio, newspapers and television.
3. To closely coordinate with the Education and Training branch to organize extensive communication activities to prevent and fight hand and foot disease in schools, especially in kindergartens and preschools on measures prevent and fight epidemics in schools, ensure that educational establishments have adequate hand-washing facilities and soap and are conveniently located to create conditions for caregivers of children and children to wash their hands frequently with soap, cleaning surfaces and toys daily with soap or regular detergent. Early detection of disease cases at educational institutions, immediately notify local health authorities to organize examination, treatment and timely treatment of outbreaks.
4. To closely monitor the situation of epidemics, promptly detect newly arising outbreaks, zoning off and thoroughly handle the outbreaks upon detection; increase sampling to identify pathogens; consolidating mobile anti-epidemic teams, mobile emergency teams ready to investigate, verify, evaluate, handle outbreaks and support lower levels in controlling outbreaks, emergency care and treatment when necessary.
5. Organizing the collection and treatment of patients well, paying attention to serious patients, minimizing the cases of serious and fatal complications. Implement good prevention of cross-contamination in hospitals and treatment facilities, especially between hand, foot and mouth disease with measles, pneumonia and other respiratory infections.
6. Proactively prepare sufficient funds to ensure the demand for drugs, supplies, chemicals and equipment for epidemic prevention and control activities. Organize training, update knowledge on disease detection surveillance and treatment at all levels to improve the capacity of health workers.
7. Regularly inspect and support the units in the area to carry out activities to prevent and control epidemics, to prevent outbreaks and spread.
- Philippines: Polio vaccination campaign, ‘Sabayang Patak Kontra Polio’, to resume in Mindanao
- Bolivia reports more than 2,000 COVID-19 cases in a day, a new record
- Quest Diagnostics receives FDA authorization to perform sample pooling for COVID-19 testing
- Routine childhood vaccines benefits far outweigh risks of additional COVID-19 transmission in Africa: Study
- Berkeley researchers: Pesticides increase Schistosomiasis transmission
- Malaria: HKUMed and Institut Pasteur collaborate to use an evolution in a test tube approach to develop new molecules for diagnosis
- Philippines COVID-19 update: 2,241 new cases, Local PCR test now available
- Ebola update: Additional case brings total to 57
- China COVID-19: Beijing under control, Epidemiologist’s take on country’s situation

