Prions can infect both humans and animals, causing Creutzfeldt-Jakob disease (CJD) in humans, mad cow disease in cattle, and chronic wasting disease in elk and deer. The infectious, misfolded protein particles often go undetected as they destroy brain tissue, causing memory loss, mobility issues, and ultimately death. Preclinical detection of prions has proven difficult, but new research suggests skin samples hold early signs of prion disease that precede neurologic symptoms.
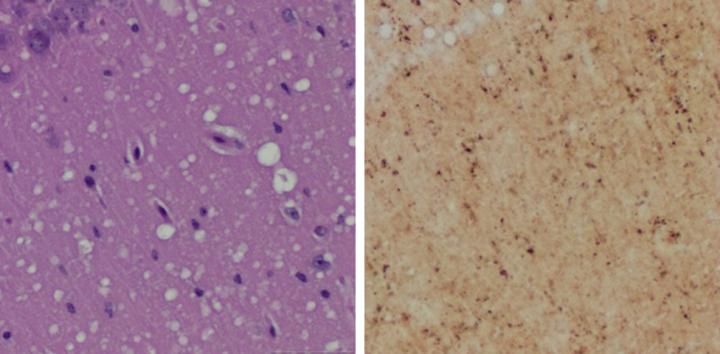
“Currently a definitive diagnosis of Creutzfeldt-Jakob disease is dependent on the examination of diseased brain tissue obtained at biopsy or autopsy. It has been impossible to detect at the early preclinical stage,” said Wenquan Zou, MD, PhD, associate professor of pathology at Case Western Reserve University School of Medicine.
In a ground-breaking study published in Nature Communications, Zou and an international team of researchers successfully used two methods to detect prions in skin samples collected from inoculated rodents. The study provides the first proof-of-concept evidence that readily accessible skin samples could be used to detect prion disease early—before clinical symptoms appear.
In the new study, Zou and colleagues successfully detected prions in rodent skin samples as early as two weeks post-infection. They also detected prions in the skin of uninoculated rodents that were housed alongside inoculated cage mates, demonstrating that prion transmission can occur between cohabitating rodents.
Read more at Case Western Reserve
- Costa Rica: Health officials investigate Hepatitis A surge in Puntarenas
- Hantavirus outbreak in Argentina: 13th fatality reported
- Liver cancer patients can be treated for Hep C infection
- Newcastle disease confirmed in Utah flock
- Infectious disease bric-a-bracs: Semen injections, Rascism allegations at WHO and African trypanosomes
- Outbreak News This Week Radio Show 1-20-19
- Arizona: Hepatitis A outbreak in Pima County
- Caribbean advised to prepare for dengue outbreak

